Renal function
Renal function, in nephrology, is an indication of the state of the kidney and its role in renal physiology. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) describes the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney. Creatinine clearance rate (CCr or CrCl) is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of creatinine per unit time and is a useful measure for approximating the GFR. Creatinine clearance exceeds GFR due to creatinine secretion, which can be blocked by cimetidine. In alternative fashion, overestimation by older serum creatinine methods resulted in an underestimation of creatinine clearance, which provided a less biased estimate of GFR.[1] Both GFR and CCr may be accurately calculated by comparative measurements of substances in the blood and urine, or estimated by formulas using just a blood test result (eGFR and eCCr).
The results of these tests are important in assessing the excretory function of the kidneys. For example, grading of chronic renal insufficiency and dosage of drugs that are excreted primarily via urine are based on GFR (or creatinine clearance).
It is commonly believed to be the amount of liquid filtered out of the blood that gets processed by the kidneys. In physiological terms, these quantities (volumetric blood flow and mass removal) are related only loosely.
Indirect markers
Most doctors use the plasma concentrations of the waste substances of creatinine and urea (U), as well as electrolytes (E), to determine renal function. These measures are adequate to determine whether a patient is suffering from kidney disease.
However, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine will not be raised above the normal range until 60% of total kidney function is lost. Hence, the more accurate Glomerular filtration rate or its approximation of the creatinine clearance is measured whenever renal disease is suspected or careful dosing of nephrotoxic drugs is required.
Another prognostic marker for kidney disease is an elevated level of protein in the urine. The most sensitive marker of proteinuria is elevated urine albumin. Persistence presence of more than 30 mg albumin per gram creatinine in the urine is diagnostic of chronic kidney disease (Microalbuminuria is a level of 30–299 mg/g; a concentration of albumin in the urine that is not detected by usual urine dipstick methods).
Glomerular filtration rate
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the volume of fluid filtered from the renal (kidney) glomerular capillaries into the Bowman's capsule per unit time.[2] Central to the physiologic maintenance of GFR is the differential basal tone of the afferent and efferent arterioles (see diagram).
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) can be calculated by measuring any chemical that has a steady level in the blood, and is freely filtered but neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the kidneys. The rate therefore measured is the quantity of the substance in the urine that originated from a calculable volume of blood. Relating this principle to the below equation - for the substance used, the product of urine concentration and urine flow equals the mass of substance excreted during the time that urine has been collected. This mass equals the mass filtered at the glomerulus as nothing is added or removed in the nephron. Dividing this mass by the plasma concentration gives the volume of plasma which the mass must have originally come from, and thus the volume of plasma fluid that has entered the bowman's capsule within the aforementioned period of time. The GFR is typically recorded in units of volume per time, e.g., milliliters per minute ml/min. Compare to filtration fraction.
There are several different techniques used to calculate or estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR or eGFR).
Measurement using inulin
The GFR can be determined by injecting inulin into the plasma. Since inulin is neither reabsorbed nor secreted by the kidney after glomerular filtration, its rate of excretion is directly proportional to the rate of filtration of water and solutes across the glomerular filter. Compared to the MDRD formula, the inulin clearance slightly overestimates the glomerular function. In early stage renal disease, the inulin clearance may remain normal due to hyperfiltration in the remaining nephrons.[3] Incomplete urine collection is an important source of error in inulin clearance measurement.
Pressure Definition
More precisely, GFR is the fluid flow rate between the glomerular capillaries and the Bowman's capsule:
Where:
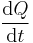 is the GFR.
is the GFR.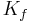 is called the filtration constant and is defined as the product of the hydraulic conductivity and the surface area of the glomerular capillaries.
is called the filtration constant and is defined as the product of the hydraulic conductivity and the surface area of the glomerular capillaries.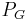 is the hydrostatic pressure within the glomerular capillaries.
is the hydrostatic pressure within the glomerular capillaries.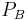 is the hydrostatic pressure within the Bowman's capsule.
is the hydrostatic pressure within the Bowman's capsule.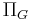 is the colloid osmotic pressure within the glomerular capillaries.
is the colloid osmotic pressure within the glomerular capillaries.- and
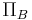 is the colloid osmotic pressure within the Bowman's capsule.
is the colloid osmotic pressure within the Bowman's capsule.
Because this constant is a measurement of hydraulic conductivity multiplied by the capillary surface area, it is almost impossible to measure physically. However, it can be determined experimentally. Methods of determining the GFR are listed in the above and below sections and it is clear from our equation that 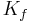 can be found by dividing the experimental GFR by the net filtration pressure:[4]
can be found by dividing the experimental GFR by the net filtration pressure:[4]
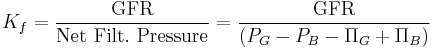
The hydrostatic pressure within the glomerular capillaries is determined by the pressure difference between the fluid entering immediately from the afferent arteriole and leaving through the efferent arteriole. The pressure difference is approximated by the product of the total resistance of the respective arteriole and the flux of blood through it:[5]
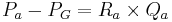
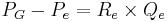
Where:
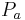 is the afferent arteriole pressure.
is the afferent arteriole pressure.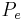 is the efferent arteriole pressure.
is the efferent arteriole pressure.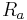 is the afferent arteriole resistance.
is the afferent arteriole resistance.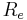 is the efferent arteriole resistance.
is the efferent arteriole resistance.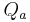 is the afferent arteriole flux.
is the afferent arteriole flux.- And,
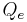 is the efferent arteriole flux.
is the efferent arteriole flux.
The pressure in the Bowman's capsule and proximal tubule can be determined by the difference between the pressure in the Bowman's capsule and the descending tubule:[5]
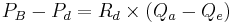
Where:
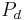 is the pressure in the descending tubule.
is the pressure in the descending tubule.- And,
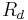 is the resistance of the descending tubule.
is the resistance of the descending tubule.
Blood plasma has a good many proteins in it and they exert an inward directed force called the colloid osmotic pressure on the water in hypotonic solutions across a membrane, i.e., in the Bowman's capsule. Because plasma proteins are virtually incapable of escaping the glomerular capillaries, this oncotic pressure is defined, simply, by the ideal gas law:[4][5]
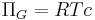
Where:
- R is the universal gas constant
- T is the temperature.
- And, c is concentration in mol/L of plasma proteins (remember the solutes can freely diffuse through the glomerular capsule).
This value is almost always taken to be equal to zero because, in a healthy nephron, there should be no proteins in the Bowman's Capsule.[4]
Creatinine-based approximations of GFR
In clinical practice, however, creatinine clearance or estimates of creatinine clearance based on the serum creatinine level are used to measure GFR. Creatinine is produced naturally by the body (creatinine is a break-down product of creatine phosphate, which is found in muscle). It is freely filtered by the glomerulus, but also actively secreted by the peritubular capillaries in very small amounts such that creatinine clearance overestimates actual GFR by 10-20%. This margin of error is acceptable, considering the ease with which creatinine clearance is measured. Unlike precise GFR measurements involving constant infusions of inulin, creatinine is already at a steady-state concentration in the blood, and so measuring creatinine clearance is much less cumbersome. However, creatinine estimates of GFR have their limitations. All of the estimating equations depend on a prediction of the 24-hour creatinine excretion rate, which is a function of muscle mass. One of the equations, the Cockcroft and Gault equation (see below) does not correct for race, and it is known that African Americans, for example, both men and women, have a higher amount of muscle mass than Caucasians; hence, African Americans will have a higher serum creatinine level at any level of creatinine clearance.
A common mistake made when just looking at serum creatinine is the failure to account for muscle mass. Hence, an older woman with a serum creatinine of 1.4 may actually have a moderately severe degree of renal insufficiency, whereas a young muscular male, in particular if African American, can have a normal level of renal function at this serum creatinine level. Creatinine-based equations should be used with caution in cachectic patients and patients with cirrhosis. They often have very low muscle mass and a much lower creatinine excretion rate than predicted by the equations below, such that a cirrhotic patient with a serum creatinine of 0.9 may have a moderately severe degree of renal insufficiency.
Creatinine Clearance CCr
One method of determining GFR from creatinine is to collect urine (usually for 24-hours) to determine the amount of creatinine that was removed from the blood over a given time interval. If one removes, say, 1440 mg in 24 hours, this is equivalent to removing 1 mg/min. If the blood concentration is 0.01 mg/mL (1 mg/dL), then one can say that 100 mL/min of blood is being "cleared" of creatinine, since, to get 1 mg of creatinine, 100 mL of blood containing 0.01 mg/mL would need to have been cleared.
Creatinine clearance (CCr) is calculated from the creatinine concentration in the collected urine sample (UCr), urine flow rate (V), and the plasma concentration (PCr). Since the product of urine concentration and urine flow rate yields creatinine excretion rate, which is the rate of removal from the blood, creatinine clearance is calculated as removal rate per min (UCr×V) divided by the plasma creatinine concentration. This is commonly represented mathematically as
Example: A person has a plasma creatinine concentration of 0.01 mg/ml and in 1 hour produces 60ml of urine with a creatinine concentration of 1.25 mg/mL.
The common procedure involves undertaking a 24-hour urine collection, from empty-bladder one morning to the contents of the bladder the following morning, with a comparative blood test then taken. The urinary flow rate is still calculated per minute, hence:
To allow comparison of results between people of different sizes, the CCr is often corrected for the body surface area (BSA) and expressed compared to the average sized man as mL/min/1.73 m2. While most adults have a BSA that approaches 1.7 (1.6-1.9), extremely obese or slim patients should have their CCr corrected for their actual BSA.
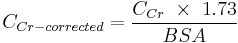
- BSA can be calculated on the basis of weight and height.
The creatinine clearance is not widely done any more, due to the difficulty in assuring a complete urine collection. When doing such a determination, to assess the adequacy of a complete collection, one always calculates the amount of creatinine excreted over a 24-hour period. This amount varies with muscle mass, and is higher in young people vs. old, in blacks vs. whites, and in men vs. women. An unexpectedly low or high 24-hour creatinine excretion rate voids the test. Nevertheless, in cases where estimates of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine are unreliable, creatinine clearance remains a useful test. These cases include "estimation of GFR in individuals with variation in dietary intake (vegetarian diet, creatine supplements) or muscle mass (amputation, malnutrition, muscle wasting), since these factors are not specifically taken into account in prediction equations."[6]
Estimated values
A number of formulae have been devised to estimate GFR or Ccr values on the basis of serum creatinine levels.
Estimated creatinine clearance rate (eCCr) using Cockcroft-Gault formula
A commonly used surrogate marker for estimate of creatinine clearance is the Cockcroft-Gault formula, which in turn estimates GFR in mL/min:[7] It is named after the scientists who first published the formula, and it employs serum creatinine measurements and a patient's weight to predict the creatinine clearance.[8][9] The formula, as originally published, is:
![eC_{Cr} = \frac { \mbox{(140 - Age)} \ \times \ \mbox{Mass (in kilograms)} \ \times \ [{0.85\ if\ Female}]} {\mbox{72} \ \times \ \mbox{Serum Creatinine (in mg/dL)}}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/46e61afd39d2a3acc66f456c33392c9e.png)
- This formula expects weight to be measured in kilograms and creatinine to be measured in mg/dL, as is standard in the USA. The resulting value is multiplied by a constant of 0.85 if the patient is female. This formula is useful because the calculations are simple and can often be performed without the aid of a calculator.
When serum creatinine is measured in µmol/L:
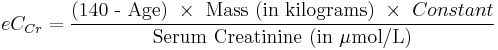
- Where Constant is 1.23 for men and 1.04 for women.
One interesting feature of the Cockcroft and Gault equation is that it shows how dependent the estimation of CCr is based on age. The age term is (140 - age). This means that a 20-year-old person (140-20 = 120) will have twice the creatinine clearance as an 80-year-old (140-80 = 60) for the same level of serum creatinine (120 is twice as great as 60). The C-G equation assumes that a woman will have a 15% lower creatinine clearance than a man at the same level of serum creatinine.
Estimated GFR (eGFR) using Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula
The most recently advocated formula for calculating the GFR is the one that was developed by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group.[10] Most laboratories in Australia,[11] and The United Kingdom now calculate and report the MDRD estimated GFR along with creatinine measurements and this forms the basis of Chronic kidney disease#Staging.[12] The adoption of the automatic reporting of MDRD-eGFR has been widely criticised.[13][14][15]
The most commonly used formula is the "4-variable MDRD," which estimates GFR using four variables: serum creatinine, age, race, and gender.[16] The original MDRD used six variables with the additional variables being the blood urea nitrogen and albumin levels.[10] The equations have been validated in patients with chronic kidney disease; however both versions underestimate the GFR in healthy patients with GFRs over 60 mL/min.[17][18] The equations have not been validated in acute renal failure.
For creatinine in mg/dL:
For creatinine in µmol/L:
![\mbox{eGFR} = \mbox{32788}\ \times \ \mbox{Serum Creatinine}^{-1.154} \ \times \ \mbox{Age}^{-0.203} \ \times \ {[1.212\ if\ Black]} \ \times \ {[0.742\ if\ Female]}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/db99b12cf04744ca85893735332b9534.png)
- Creatinine levels in µmol/L can be converted to mg/dL by dividing them by 88.4. The 32788 number above is equal to 186×88.41.154.
A more elaborate version of the MDRD equation also includes serum albumin and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels:
![\mbox{eGFR} = \mbox{170}\ \times \ \mbox{Serum Creatinine}^{-0.999} \ \times \ \mbox{Age}^{-0.176} \ \times \ {[0.762\ if\ Female]} \ \times \ {[1.180\ if\ Black]} \ \times \ \mbox{BUN}^{-0.170} \ \times \ \mbox{Albumin}^{%2B0.318}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/727fb222d37012663ab0c148d375dba6.png)
- Where the creatinine and blood urea nitrogen concentrations are both in mg/dL. The albumin concentration is in g/dL.
These MDRD equations are to be used only if the laboratory has NOT calibrated its serum creatinine measurements to isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS). When IDMS-calibrated serum creatinine is used (which is about 6% lower), the above equations should be multiplied by 175/186 or by 0.94086.[19]
Since these formulae do not adjust for body mass, they (relative to the Cockcroft-Gault formula) underestimate eGFR for heavy people and overestimate it for underweight people. (see Cockcroft-Gault formula above).
Estimated GFR (eGFR) using the CKD-EPI formula
The CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) formula was published in May 2009. It was developed in an effort to create a formula more accurate than the MDRD formula, especially when actual GFR is greater than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Researchers pooled data from multiple studies to develop and validate this new equation. They used 10 studies that included 8254 participants, randomly using 2/3 of the data sets for development and the other 1/3 for internal validation. Sixteen additional studies, which included 3896 participants, were used for external validation.
The CKD-EPI equation performed better than the MDRD (Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study) equation, especially at higher GFR, with less bias and greater accuracy. When looking at NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) data, the median estimated GFR was 94.5 mL/min per 1.73 m2 vs. 85.0 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and the prevalence of chronic kidney disease was 11.5% versus 13.1%.
The CKD-EPI equation, expressed as a single equation, is:
where SCr is serum creatinine (mg/dL), k is 0.7 for females and 0.9 for males, a is -0.329 for females and -0.411 for males, min indicates the minimum of SCr/k or 1, and max indicates the maximum of SCr/k or 1.
A clearer version may be as follows: For creatinine (IDMS calibrated) in mg/dL:
African American Female
If serum creatinine (Scr) <= 0.7
If serum creatinine (Scr) > 0.7
African American Male
If serum creatinine (Scr) <= 0.9
If serum creatinine (Scr) > 0.9
White or other race Female
If serum creatinine (Scr) <= 0.7
If serum creatinine (Scr) > 0.7
White or other race Male
If serum creatinine (Scr) <= 0.9
If serum creatinine (Scr) > 0.9
This formula was developed by Levey et al.[20]
The formula CKD-EPI may provide improved cardiovascular risk prediction over the MDRD Study formula in a middle-age population.[21]
Estimated GFR (eGFR) using the Mayo Quadratic formula
Another estimation tool to calculate GFR is the Mayo Quadratic formula. This formula was developed by Rule et al.[17] in an attempt to better estimate GFR in patients with preserved kidney function. It is well recognized that the MDRD formula tends to underestimate GFR in patients with preserved kidney function.
The equation is:
If Serum Creatinine < 0.8 mg/dL, use 0.8 mg/dL for Serum Creatinine
Estimated GFR for children using Schwartz formula
In children, the Schwartz formula is used.[22][23] This employs the serum creatinine (mg/dL), the child's height(cm) and a constant to estimate the glomerular filtration rate:
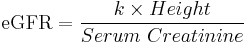
- Where k is a constant that depends on muscle mass, which itself varies with a child's age:
The method of selection of the K-constant value has been questioned as being dependent upon the gold-standard of renal function used (i.e., creatinine clearance, inulin clearance, etc.) and also may be dependent upon the urinary flow rate at the time of measurement.[25]
In 2009, the formula was updated to use standardized serum creatinine (recommend k=0.413) and additional formulas that allow improved precision were derived if serum cystatin measured in addition to serum creatinine.[26]
Importance of calibration of the serum creatinine level and the IDMS standardization effort
One problem with any creatinine-based equation for GFR is that the methods used to assay creatinine in the blood differ widely in their susceptibility to non-specific chromogens, which cause the creatinine value to be overestimated. In particular, the MDRD equation was derived using serum creatinine measurements that had this problem. The NKDEP program in the United States has attempted to solve this problem by trying to get all laboratories to calibrate their measures of creatinine to a "gold standard", which in this case is isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS). At the present time in late 2009 not all labs in the U.S. have changed over to the new system. There are two forms of the MDRD equation that are available, depending on whether or not creatinine was measured by an IDMS-calibrated assay. The CKD-EPI equation is designed to be used with IDMS-calibrated serum creatinine values only.
Cystatin C
Problems with creatinine (varying muscle mass, recent meat ingestion, etc.) have led to evaluation of alternative agents for estimation of GFR. One of these is cystatin C, a ubiquitous protein secreted by most cells in the body (it is an inhibitor of cysteine protease).
Cystatin C is freely filtered at the glomerulus. After filtration, Cystatin C is reabsorbed and catabolized by the tubular epithelial cells, with only small amounts excreted in the urine. Cystatin C levels are therefore measured not in the urine, but in the bloodstream.
Equations have been developed linking estimated GFR to serum cystatin C levels. Most recently, some proposed equations have combined creatinine and cystatin.[27]
Normal ranges
The normal range of GFR, adjusted for body surface area, is similar in men and women, and is in the range of 100-130 ml/min/1.73m2. In children, GFR measured by inulin clearance remains close to about 110 ml/min/1.73m2 down to about 2 years of age in both sexes, and then it progressively decreases. After age 40, GFR decreases progressively with age, by about 0.4 - 1.2 mL/min per year.
Chronic kidney disease stages
Risk factors for kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, family history, older age, ethnic group and smoking. For most patients, a GFR over 60 mL/min/1.73m2 is adequate. But significant decline of the GFR from a previous test result can be an early indicator of kidney disease requiring medical intervention. The sooner kidney dysfunction is diagnosed and treated the greater odds of preserving remaining nephrons, and preventing the need for dialysis.
The severity of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is described by six stages; the most severe three are defined by the MDRD-eGFR value, and first three also depend on whether there is other evidence of kidney disease (e.g., proteinuria):
- 0) Normal kidney function – GFR above 90mL/min/1.73m2 and no proteinuria
- 1) CKD1 – GFR above 90mL/min/1.73m2 with evidence of kidney damage
- 2) CKD2 (Mild) – GFR of 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73m2 with evidence of kidney damage
- 3) CKD3 (Moderate) – GFR of 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73m2
- 4) CKD4 (Severe) – GFR of 15 to 29 mL/min/1.73m2
- 5) CKD5 Kidney failure - GFR less than 15 mL/min/1.73m2 Some people add CKD5D for those stage 5 patients requiring dialysis; many patients in CKD5 are not yet on dialysis.
Note: others add a "T" to patients who have had a transplant regardless of stage.
Not all clinicians agree with the above classificaiton, suggesting that it may overlabel patients with mildly reduced kidney function, especially the elderly, as having a disease.[28][29] A conference was held in 2009 regarding these controversies by Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) on CKD: Definition, Classification and Prognosis, gathering data on CKD prognosis to refine the definition and staging of CKD.[30]
See also
- Clearance
- Dialysis
- Filtration fraction
- Kt/V
- Pharmacokinetics
- Renal clearance ratio
- Renal failure
- Standardized Kt/V
- Tubuloglomerular feedback
- Urea reduction ratio
References
- ^ Stevens LA, Coresh J, Greene T, Levey AS (June 2006). "Assessing kidney function--measured and estimated glomerular filtration rate". The New England Journal of Medicine 354 (23): 2473–83. doi:10.1056/NEJMra054415. PMID 16760447.
- ^ Physiology at MCG 7/7ch04/7ch04p11 - "Glomerular Filtration Rate"
- ^ GFR (Cockcroft & MDRD) calculator at medical-calculator.nl - Cockcroft and MDRD calculator and details about inulin clearance
- ^ a b c d Guyton, Arthur; Hall, John (2006). "Chapter 26: Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow, and Their Control". In Gruliow, Rebecca (in English) (Book). Textbook of Medical Physiology (11th ed.). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Elsevier Inc.. pp. 308–325. ISBN 0-7216-0240-1.
- ^ a b c d Keener, James; Sneyd, James (2004). "20: Renal Physiology". In Marsden, J.E. (in English) (Book). Mathematical Physiology. Interdisciplinary Mathematics. Mathematical Biology Vol. 8. Sirovich, Wiggins (1st ed.). New York, NY: Springer Science +Business Media LLC. pp. 612–636. ISBN 0-387-98381-3.
- ^ "KDOQI CKD Guidelines". http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/guidelines_ckd/p5_lab_g4.htm. Retrieved 2010-08-25.
- ^ GFR Calculator at cato.at - Cockcroft-Gault - GFR calculation (Cockcroft-Gault formula)
- ^ Cockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976). "Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine". Nephron 16 (1): 31–41. doi:10.1159/000130554. PMID 1244564.
- ^ Gault MH, Longerich LL, Harnett JD, Wesolowski C (1992). "Predicting glomerular function from adjusted serum creatinine". Nephron 62 (3): 249–56. doi:10.1159/000187054. PMID 1436333.
- ^ a b Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (March 1999). "A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group". Annals of Internal Medicine 130 (6): 461–70. PMID 10075613. http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10075613.
- ^ Mathew TH, Johnson DW, Jones GR (October 2007). "Chronic kidney disease and automatic reporting of estimated glomerular filtration rate: revised recommendations". The Medical Journal of Australia 187 (8): 459–63. PMID 17937643. http://www.mja.com.au/public/issues/187_08_15/10/07/mat10525_fm.html.
- ^ Joint Specialty Committee on Renal Disease (June 2005). "Chronic kidney disease in adults: UK guidelines for identification, management and referral" (PDF). http://www.renal.org/CKDguide/full/UKCKDfull.pdf.
- ^ Davey RX (January 2006). "Chronic kidney disease and automatic reporting of estimated glomerular filtration rate". The Medical Journal of Australia 184 (1): 42–3; author reply 43. PMID 16398632. http://www.mja.com.au/public/issues/184_01_/02/01/06/matters_arising_020106_fm-6.html.
- ^ Twomey PJ, Reynolds TM (November 2006). "The MDRD formula and validation". QJM 99 (11): 804–5. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcl108. PMID 17041249.
- ^ Kallner A, Ayling PA, Khatami Z (2008). "Does eGFR improve the diagnostic capability of S-Creatinine concentration results? A retrospective population based study". International Journal of Medical Sciences 5 (1): 9–17. PMC 2204044. PMID 18219370. http://www.medsci.org/v05p0009.htm.
- ^ National Kidney Foundation (February 2002). "K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification". American Journal of Kidney Diseases 39 (2 Suppl 1): S1–266. doi:10.1016/S0272-6386(02)70081-4. PMID 11904577.
- ^ a b Rule AD, Larson TS, Bergstralh EJ, Slezak JM, Jacobsen SJ, Cosio FG (December 2004). "Using serum creatinine to estimate glomerular filtration rate: accuracy in good health and in chronic kidney disease". Annals of Internal Medicine 141 (12): 929–37. PMID 15611490.
- ^ Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T et al. (August 2006). "Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate". Annals of Internal Medicine 145 (4): 247–54. PMID 16908915.
- ^ "GFR MDRD Calculator for Adults". National Kidney Disease Education Program. United States: National Institutes of Health. http://www.nkdep.nih.gov/professionals/gfr_calculators/idms_con.htm.
- ^ Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH et al. (May 2009). "A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate". Annals of Internal Medicine 150 (9): 604–12. PMC 2763564. PMID 19414839. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2763564.
- ^ Matsushita K, Selvin E, Bash LD, Astor BC, Coresh J (April 2010). "Risk implications of the new CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation compared with the MDRD Study equation for estimated GFR: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study". American Journal of Kidney Diseases 55 (4): 648–59. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.12.016. PMC 2858455. PMID 20189275. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2858455.
- ^ a b Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM, Spitzer A (August 1976). "A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine". Pediatrics 58 (2): 259–63. PMID 951142.
- ^ a b Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ (June 1984). "A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life". The Journal of Pediatrics 104 (6): 849–54. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(84)80479-5. PMID 6726515.
- ^ Brion LP, Fleischman AR, McCarton C, Schwartz GJ (October 1986). "A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in low birth weight infants during the first year of life: noninvasive assessment of body composition and growth". The Journal of Pediatrics 109 (4): 698–707. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(86)80245-1. PMID 3761090.
- ^ Haenggi MH, Pelet J, Guignard JP (February 1999). "[Estimation of glomerular filtration rate by the formula GFR = K x T/Pc]" (in French). Archives De Pédiatrie 6 (2): 165–72. doi:10.1016/S0929-693X(99)80204-8. PMID 10079885.
- ^ Schwartz GJ, Muñoz A, Schneider MF et al. (March 2009). "New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 20 (3): 629–37. doi:10.1681/ASN.2008030287. PMC 2653687. PMID 19158356. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2653687.
- ^ Stevens LA, Coresh J, Schmid CH et al. (March 2008). "Estimating GFR using serum cystatin C alone and in combination with serum creatinine: a pooled analysis of 3,418 individuals with CKD". American Journal of Kidney Diseases 51 (3): 395–406. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.11.018. PMC 2390827. PMID 18295055. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2390827.
- ^ Bauer C, Melamed ML, Hostetter TH (2008). "Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease: Time for a Course Correction". American Society of Nephrology 19 (5): 844–46. doi:10.1681/ASN.2008010110. http://jasn.asnjournals.org/content/19/5/844.full.
- ^ Eckardt K-U, Berns JS, Rocco MV, Kasiske BL (June 2009). "Definition and Classification of CKD: The Debate Should Be About Patient Prognosis—A Position Statement From KDOQI and KDIGO" (PDF). American Journal of Kidney Diseases 53 (6): 915–920. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.04.001. PMID 19406541. http://www.kdigo.org/meetings_events/pdf/KDOQI-KDIGO_Editorial_on_CKD_Classification.pdf.
- ^ "KDIGO Controversies Conference: Definition, Classification and Prognosis in CKD, London, October 2009". Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). 2009. http://www.kdigo.org/meetings_events/CKD_Controversies_Conference.php.
External links
Online GFR Calculators
- Online calculator that combines a variety of estimation methods
- MDRD/CKD-EPI calculator provided by the Nephron Information Center
- Online GFR Calculator for chemotherapy dosing
- Schwartz formula for estimating pediatric renal function
Reference links
- National Kidney Disease Education Program website. Includes professional references and GFR calculators
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

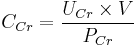
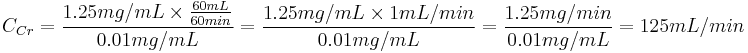
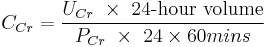
![\mbox{eGFR} = \mbox{186}\ \times \ \mbox{Serum Creatinine}^{-1.154} \ \times \ \mbox{Age}^{-0.203} \ \times \ {[1.212\ if\ Black]} \ \times \ {[0.742\ if\ Female]}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/2af94a4226aee0d827f876fde8f138c0.png)
![\mbox{eGFR} = \mbox{141}\ \times \ \mbox{min(SCr/k,1)}^{a} \ \times \ \mbox{max(SCr/k,1)}^{-1.209} \ \times \ \mbox{0.993}^{Age} \ \times \ {[1.018\ if\ Female]} \ \times \ {[1.159\ if\ Black]} \](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/46b8ff7c0e46ef484446555d2c23b423.png)
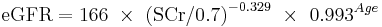
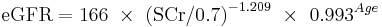
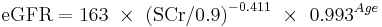
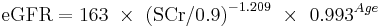
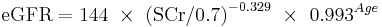
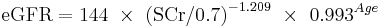
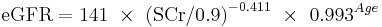
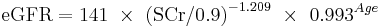
![\mbox{eGFR} = \mbox{exp}{(1.911%2B 5.249/{Serum\ Creatinine} - 2.114/{Serum\ Creatinine}^2 - 0.00686 \ \times \ \mbox{Age} - {[0.205\ if\ Female]})}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/88f67e900e9c92f55e31c925b5ea3ab3.png)